
자바스크립트 면접시 가장 많이 물어본 20가지 문답
머신러닝과 웹개발 전문가 Mayank에게 감사합니다.
본문 (트위터: https://twitter.com/nlognco/status/1282888619917627393?s=20)
※영어주의※ ->구글번역기
1. What's the difference between undefined and null?
"undefined" is the default value of a variable that has not been assigned a specific value and "null" is a value that represents no value.
2. What does the && operator do?
The && or Logical AND operator finds the first falsy expression in its operands and returns it and if it does not find any falsy expression it returns the last expression.
3. What does the || operator do?
The || or Logical OR operator finds the first truthy expression in its operands and returns it. This too employs short-circuiting to prevent unnecessary work.
4. What is DOM?
DOM stands for Document Object Model is an interface (API) for HTML and XML documents. When the browser first reads our HTML document it creates a big object, a really big object based on the HTML document this is the DOM.
5. What is Event Propagation?
Event propagation is a mechanism that defines how events propagate or travel through the DOM tree to arrive at its target and what happens to it afterward.
6. What's Event Bubbling?
In the Bubbling Phase, the event bubbles up or it goes to its parent, to its grandparents, to its grandparent's parent until it reaches all the way to the window.
7. What's Event Capturing?
In Capturing Phase, the event starts from the window all the way down to the element that triggered the event.
8. What is event.target ?
The event.target is the element on which the event occurred or the element that triggered the event.
9. What's the difference between == and === ?
The difference between ==(abstract equality) and ===(strict equality) is that the == compares by value after coercion and === compares by value and type without coercion.
10. Why does it return false when comparing two similar objects in JavaScript?
JavaScript compares objects and primitives differently. In primitives, it compares them by value while in objects it compares them by reference or the address in memory where the variable is stored.
11. What does the !! operator do?
The Double NOT operator or !! coerces the value on the right side into a boolean. Basically, it's a fancy way of converting a value into a boolean.
12. How to evaluate multiple expressions in one line?
We can use the , or comma operator to evaluate multiple expressions in one line. It evaluates from left-to-right. Example - x = (x++ , x = addFive(x), x *= 2, x -= 5, x += 10);
13. What is Hoisting?
Hoisting is the term used to describe the moving of variables and functions to the top of their (global or function) scope on where we define that variable or function.
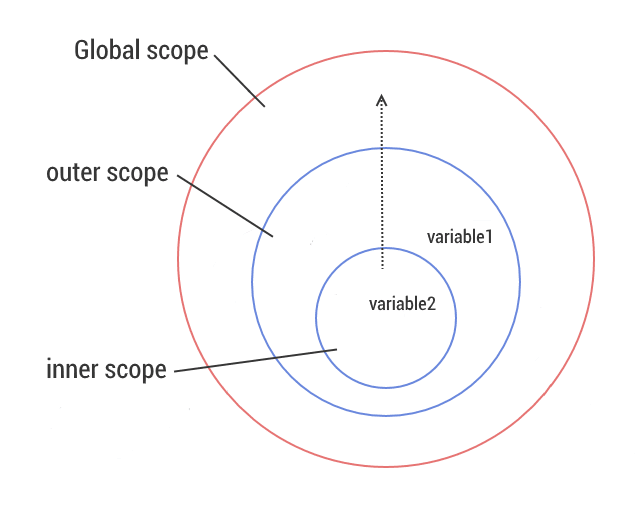
14. What is Scope?
Scope in JavaScript is the area where we have valid access to variables or functions. JavaScript has three types of Scopes - 1. Global Scope 2. Function Scope 3. Block Scope(ES6).
15. What are the falsy values in JavaScript?
falsy values are values that when converted to boolean becomes false.
16. What does "use strict" do?
"use strict" is an ES5 feature in JavaScript that makes our code in Strict Mode in functions or entire scripts. Strict Mode helps us avoid bugs early on in our code and adds restrictions to it.
17. What's the value of this in JavaScript?
"this" refers to the value of the object that is currently executing or invoking the function.
18. What is the prototype of an object?
A prototype in simplest terms is a blueprint of an object. It is used as a fallback for properties and methods if it does exist in the current object. It's the way to share properties and functionality between objects.
19. What are Higher Order Functions?
Higher-Order Function is functions that can return a function or receive argument or arguments which have a value of a function.
20. What's the difference between var, let, and const keywords?
Variables declared with "var" keyword are function scoped. Variables declared with "let" and "const" keyword are block-scoped. Difference b/w let & const we can assign new values using let but we can't in const
'Web Dev > JavaScript :: 자바스크립트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Javascript] if문은 ternary 그리고 '&&'로 바꿀수 있다 (0) | 2020.09.21 |
|---|---|
| [JavaScript] DOM 끝장내기 코스 추천 [영어] (0) | 2020.08.25 |
| [Javascript] String.fromCharCode() 숫자를 문자로! (0) | 2020.07.01 |
| [Javascript] 즉각 실행되는 IIFE (0) | 2020.06.21 |
| [Javascript] 클로저 closure 이란? (0) | 2020.06.21 |